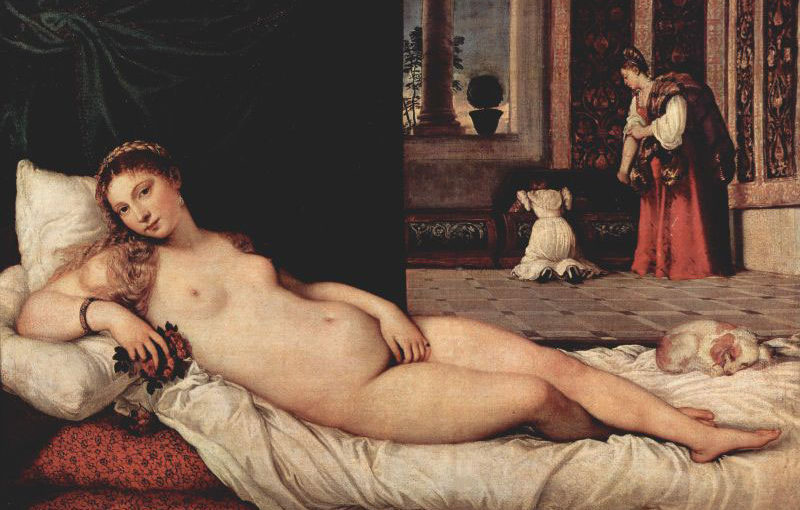
Formal analysis is the interpretation and explanation of an artwork. When referring to formal analysis, the analyst considers different components identified in the work, and then draws out a summary of their findings. There are many components to formal analysis. Some examples include: historical context, materials, color schemes, and composition. Historical context is one the most important part in conducting a formal analysis. Understanding circumstances surrounding the time period the art was created, can give an indication to the analysis what exactly the artist was trying to convey and why certain elements, such as colors, expressions, and/or techniques, were used in the final product. Colors in general play a huge part in influencing the emotions of the viewer. Depending on the intended emotion, the artist will use specific colors that correlate with said emotion. For example, when using dark, dreary colors in art, this often gives the viewer a sense of sadness or even tragic, depending the contexts of artwork. Composition is arrangement of elements in an artwork. It can be used to bring attention to a specific element, contrast the context, convey depth in 2-dimensional art, or to bring the whole painting together. These components and many others when interpreted together, give a formal analysis that provides a better understand of the artwork as well as the artist and their mindset.